Die Casting vs CNC Machining: Which Manufacturing Process Will Save You More Time and Money in 2024?
Die Casting vs CNC Machining: Which Manufacturing Process Will Save You More Time and Money in 2024?

In today's competitive manufacturing landscape, choosing the right production method can make or break your project's success. As manufacturers face increasing pressure to deliver high-quality parts quickly and cost-effectively, the decision between die casting and CNC machining becomes crucial for project success.
Manufacturing decision-makers often struggle with balancing cost, quality, and production speed. Die casting and CNC machining each offer unique advantages, but understanding which process best suits your specific needs can significantly impact your bottom line and project timeline.
Before diving deep into each manufacturing method, it's important to understand that both processes have established themselves as cornerstones of modern manufacturing, each serving distinct purposes and industries. Let's explore their key differences, costs, and applications to help you make an informed decision.
[Table of Contents]
- What Are the Fundamental Differences Between Die Casting and CNC Machining?
-
How Do Production Costs Compare Between Die Casting and CNC Machining?
-
Which Process Offers Better Quality and Precision Standards?
- What Industries Benefit Most From Each Manufacturing Method?
-
Conclusion
What Are the Fundamental Differences Between Die Casting and CNC Machining?
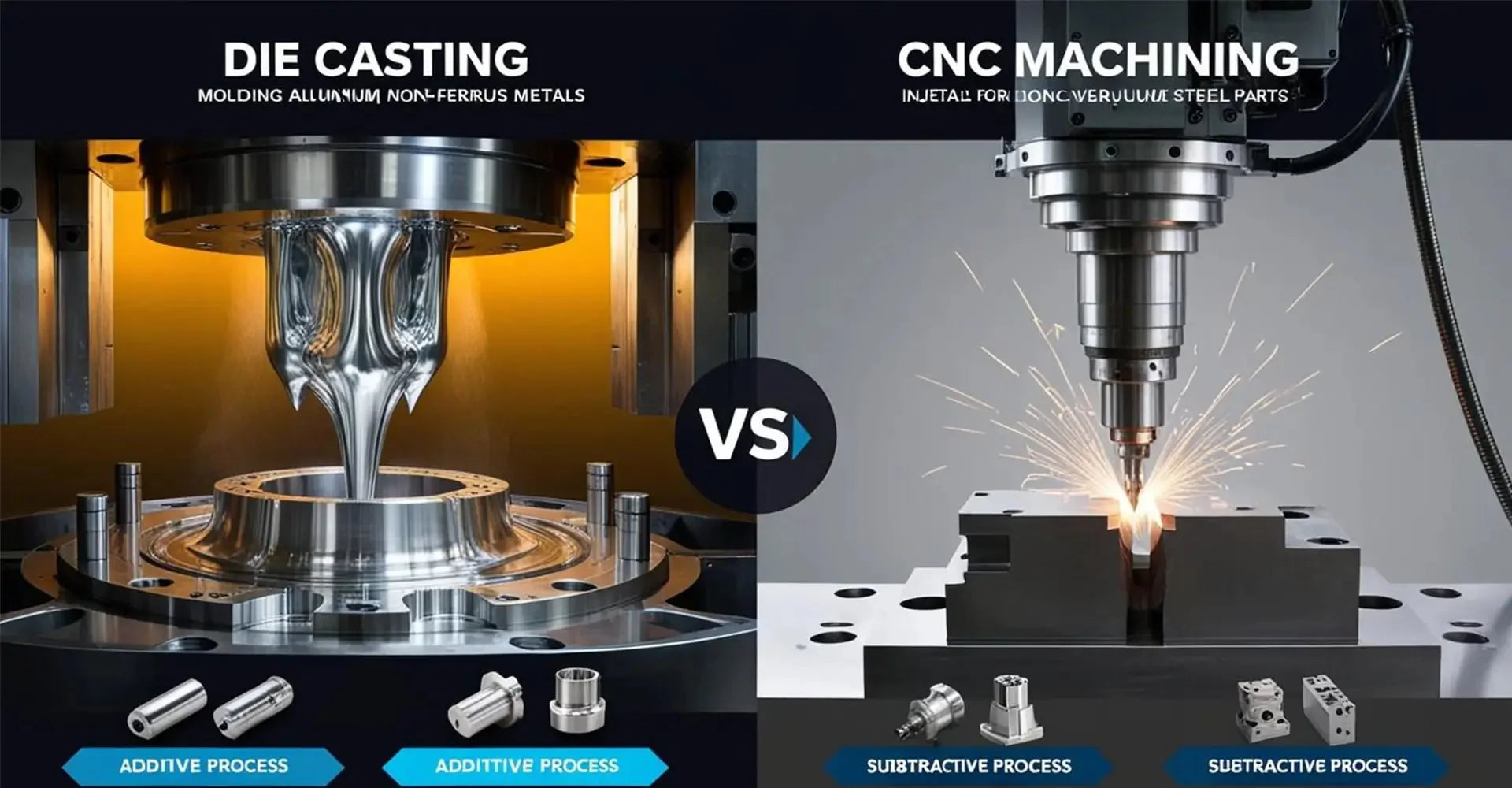
Die casting involves injecting molten metal into precisely engineered molds under high pressure, creating complex parts in a single operation. Meanwhile, CNC machining utilizes computer-controlled cutting tools to remove material from solid blocks, offering exceptional precision and flexibility.
The fundamental contrast lies in their approach: die casting is an additive process where material is added to create parts, while CNC machining is subtractive, removing material to achieve the desired shape. This distinction significantly impacts material selection, production efficiency, and cost structures.

When examining material compatibility, die casting typically works with non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium, making it ideal for kitchen appliances and consumer products. In contrast, CNC machining can handle a broader range of materials, including various metals, plastics, and composites, making it versatile for industrial machinery components.
How Do Production Costs Compare Between Die Casting and CNC Machining?
Initial investment and production volume play crucial roles in determining cost-effectiveness. Die casting requires significant upfront investment in mold design and creation, often ranging from $10,000 to $100,000, but offers lower per-unit costs in high-volume production.
The cost structure breaks down differently for each method:
- Die Casting: High initial tooling costs + Low per-unit cost
- CNC Machining: Minimal setup costs + Higher per-unit cost
For production volumes exceeding 10,000 units, die casting typically becomes more cost-effective. However, CNC machining remains economical for lower volumes and prototyping phases, particularly in the automotive sector where design iterations are frequent.
Which Process Offers Better Quality and Precision Standards?
Quality control and precision capabilities vary significantly between these manufacturing methods. CNC machining excels in achieving tight tolerances, often reaching ±0.0005 inches, making it ideal for electronics manufacturing.
Die casting can consistently produce parts with tolerances of ±0.002 inches, suitable for most commercial applications. However, surface finish quality differs:

The precision debate extends beyond mere measurements. Die casting excels in reproducing complex internal geometries, while CNC machining offers superior control over external features and dimensional accuracy.
What Industries Benefit Most From Each Manufacturing Method?
Different industries leverage these manufacturing processes based on their specific requirements and production volumes.
Die casting dominates in:
- Automotive components
- Consumer electronics housings
- Kitchen appliance parts
- Lighting fixtures
CNC machining prevails in:
- Aerospace components
- Medical devices
- Custom machinery parts
- Prototype development
As manufacturing technology evolves, we're seeing increased integration of both methods in hybrid manufacturing approaches, particularly in industries requiring both high volume and precision.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Manufacturing Needs
Selecting between die casting and CNC machining requires careful consideration of multiple factors:
- Production volume requirements
- Budget constraints
- Quality specifications
- Material requirements
- Time to market
For high-volume production with complex geometries, die casting often proves most cost-effective. Conversely, CNC machining remains the go-to choice for lower volumes, prototypes, and parts requiring exceptional precision.
[External Links Recommendation]
- CNC Machining Cost: How to Calculate & Reduce its Cost?
-
CNC Machining Cost - Fathom Digital Manufacturing
-
CNC Machining vs Die Casting – Which is Better?
- Die Casting vs. CNC Machining: Which is better for Your Project?
-
How do Die Casting and CNC Machining Compare?





