What's The Best Choice Between Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting For Your Manufacturing Project?
What's The Best Choice Between Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting For Your Manufacturing Project?

Choosing between zinc and aluminum die casting can significantly impact your manufacturing project's success. As manufacturing complexities increase, selecting the right material becomes crucial for achieving optimal performance, cost efficiency, and product quality.
According to recent market data, the aluminum die casting market stands at $107.22 billion, while the zinc die casting sector represents $4.28 billion in 2024. These figures reflect the widespread adoption of both materials across various industries, each serving distinct manufacturing needs.
Both zinc and aluminum die casting offer unique advantages for different applications. Whether you're developing automotive components, industrial machinery, or consumer products, understanding the key differences between these materials will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your project requirements.
[Table of Contents]
- What Are The Critical Material Properties That Set Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting Apart?
- How Do Production Costs Compare Between Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting?
- Which Industries Benefit Most From Each Die Casting Method?
- What Are The Design Capabilities and Limitations of Each Material?
What Are The Critical Material Properties That Set Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting Apart?
The fundamental differences between zinc and aluminum die casting lie in their physical and mechanical properties. Understanding these distinctions is essential for selecting the optimal material for your die casting project.
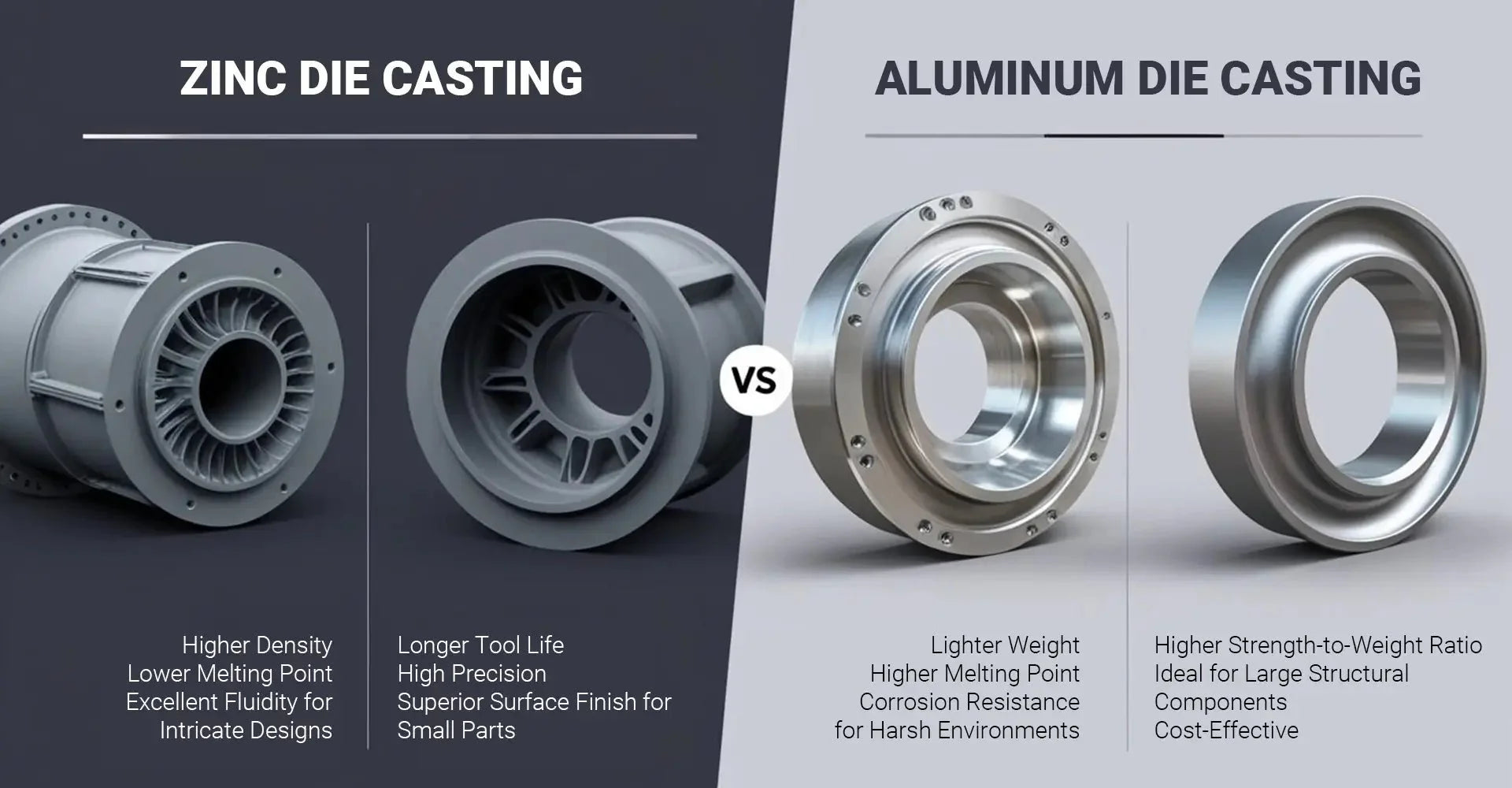
Material properties significantly influence manufacturing processes, product performance, and overall project costs. Zinc's density of ~5 g/cm³ contrasts with aluminum's ~2.7 g/cm³, while their melting points differ by approximately 240°C.

These distinct characteristics affect everything from tool life to production efficiency. Zinc's lower melting point enables faster production cycles and more intricate designs, while aluminum's lighter weight makes it ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial. When combined with CNC machining services, both materials can achieve exceptional precision and surface quality.
How Do Production Costs Compare Between Zinc and Aluminum Die Casting?
Cost considerations extend beyond basic material prices to encompass the entire production lifecycle. Understanding these factors helps in making a cost-effective choice for your manufacturing project.
While aluminum typically offers lower material costs, zinc die casting can achieve significant savings through extended tool life - up to 1,000,000 shots compared to aluminum's 100,000 shots. Additionally, surface finish requirements can impact final costs substantially.
The total cost analysis must consider factors such as energy consumption, cycle times, and maintenance requirements. Zinc's faster cycle times can lead to higher production efficiency, while aluminum's lower material costs might benefit larger components. The choice ultimately depends on production volume, part size, and specific project requirements.
Which Industries Benefit Most From Each Die Casting Method?
Different industries leverage the unique advantages of zinc and aluminum die casting to meet their specific requirements. The automotive sector, in particular, utilizes both materials extensively.
Zinc die casting excels in applications requiring high precision and strength, while aluminum dominates in scenarios where weight reduction is crucial. Both materials find extensive use in industrial machinery applications.
The automotive industry often chooses aluminum for structural components and engine parts, while zinc is preferred for detailed components like door handles and trim pieces. Electronics manufacturers typically opt for zinc in small, intricate components where precision is paramount.
What Are The Design Capabilities and Limitations of Each Material?
Design possibilities vary significantly between zinc and aluminum die casting, affecting everything from wall thickness to surface finish quality.
Zinc offers superior capabilities for thin walls and complex geometries, while aluminum provides excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. Understanding these limitations is crucial for optimizing your design.
Zinc's excellent fluidity allows for more intricate designs and thinner walls, making it ideal for complex, detailed components. Aluminum's properties make it better suited for larger structural parts where strength and weight are critical factors.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Die Casting Choice
The success of your die casting project depends on carefully weighing material properties, production costs, industry requirements, and design considerations. Consider these key factors:
- Material properties and their impact on product performance
- Total production costs including tooling and maintenance
- Industry-specific requirements and standards
- Design complexity and dimensional requirements
Making Your Decision
Select zinc die casting when you need:
- High precision and intricate details
- Extended tool life
- Superior surface finish
- Fast production cycles
Choose aluminum die casting for:
- Lightweight applications
- High-temperature environments
- Large structural components
- Cost-effective large-volume production
External Links
[zinc die casting](https://decoprod.com/zinc-advantages-in-die-casting/)[^1]
[aluminum die casting](https://www.phbcorp.com/what-is-aluminum-die-casting/)[^2]
[zinc vs aluminum die casting](https://www.tfgusa.com/aluminum-die-casting-vs-zinc-die-casting/)[^3]
---
[^1]: Explore the advantages of zinc die casting to understand its applications and benefits in manufacturing.
[^2]: Learn about the various applications of aluminum die casting and how it compares to other materials.
[^3]: Discover the key differences between zinc and aluminum die casting to make informed decisions for your projects.
-
Posted in
die casting





