EDM vs CNC Milling: Which Process Is Best For Your Precision Parts?
EDM vs CNC Milling: Which Process Is Best For Your Precision Parts?

Making the Right Choice for Your Manufacturing Needs
When it comes to precision manufacturing, choosing between Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling can significantly impact your project's success. Moreover, this decision affects everything from production timelines to part quality and overall costs. Understanding the EDM vs CNC Milling comparison is crucial for engineers and procurement specialists alike.
Quick Answer: EDM excels at machining extremely hard materials and complex internal geometries with exceptional accuracy, while CNC milling offers faster production times, lower setup costs, and greater material versatility. Your specific part requirements, including material type, geometric complexity, and surface finish needs, should guide your decision between these two complementary processes.
Before diving into the detailed comparison, it's important to note that these technologies aren't always competing alternatives. In fact, many sophisticated manufacturing operations leverage both methods at different stages of production. Throughout this guide, we'll examine the strengths and limitations of each process to help you make informed decisions for your specific applications.
Table of Contents
- How Does Material Hardness Affect Your Machining Process Selection?
- Can Your Part's Complex Geometry Be Machined Economically?
- What Are The Real Cost Factors When Choosing Between EDM and CNC?
- Which Process Delivers The Surface Finish Your Application Needs?
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
How Does Material Hardness Affect Your Machining Process Selection?
When evaluating manufacturing processes, material hardness emerges as a primary consideration that can immediately narrow your options. Precision machining: Electrical Discharge vs CNC milling capabilities differ dramatically when working with hardened materials.
EDM shines when working with hardened steel (HRC 60+) and exotic alloys like Inconel, Hastelloy, and titanium. Since EDM uses thermal energy rather than mechanical force, material hardness has minimal impact on machining effectiveness. This makes EDM particularly valuable for aerospace, medical, and defense applications where high-strength materials are standard requirements.

Delving deeper into material considerations, EDM's non-contact process eliminates mechanical stress, tool deflection, and vibration issues that plague conventional CNC milling of hardened materials. This characteristic makes EDM the go-to solution for hard material machining solutions for complex geometries. While CNC milling can certainly process hardened materials, it typically requires specialized carbide or ceramic tooling, reduced cutting speeds, and more frequent tool changes—all factors that increase production time and costs.
Can Your Part's Complex Geometry Be Machined Economically?
Geometry complexity often determines which manufacturing process provides the most economical solution for your precision components. Understanding each method's capabilities can prevent costly production challenges.
EDM wire cutting achieves exceptional accuracy for internal corners (±0.005mm) and can produce sharp internal features impossible with rotary cutting tools. Meanwhile, advanced 5-axis CNC milling delivers impressive ±0.01mm accuracy for complex 3D contours while operating at significantly faster material removal rates for external features.
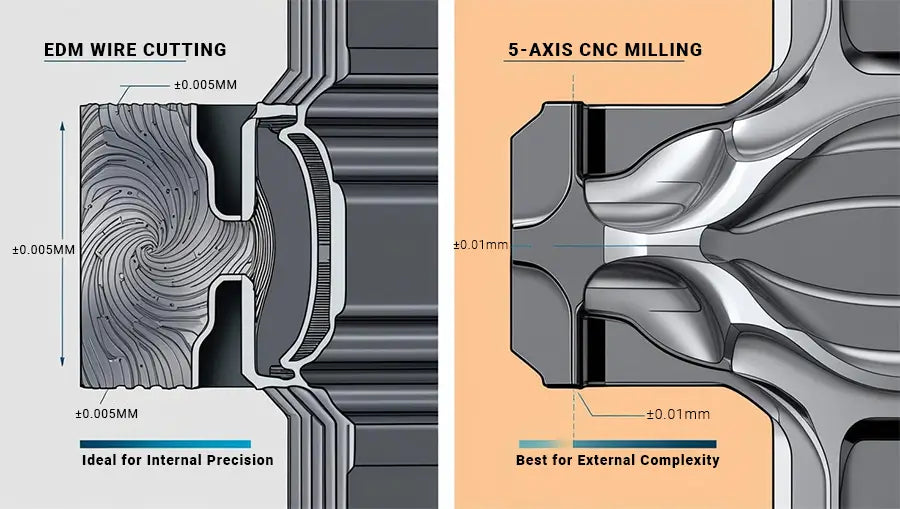
When examining complex part requirements more closely, EDM offers unmatched advantages for internal sharp corners, narrow slots (down to 0.1mm), and intricate internal profiles—all with minimal setup constraints. Conversely, modern CNC milling services excel at creating complex external geometries, undercuts, and organic shapes. The selection often comes down to specific feature requirements—internal precision favors EDM, while external complexity and speed requirements typically favor CNC solutions.
What Are The Real Cost Factors When Choosing Between EDM and CNC?
Understanding the complete cost structure of each manufacturing process helps prevent budget surprises and enables more accurate quotations for your customers.
The cost of EDM wire cutting vs CNC milling involves distinct expense patterns. EDM requires significant initial investment for electrode fabrication (often $200+ per unique electrode) but experiences minimal tool wear during operation. In contrast, CNC milling offers lower setup costs but incurs ongoing cutter replacement expenses (approximately $50/hr for titanium machining) that accumulate throughout production.
Analyzing production economics more thoroughly reveals that for small batches of hardened materials, EDM's higher initial costs are often offset by its ability to run unattended for extended periods. For larger production runs of more machinable materials, CNC's higher material removal rates and lower setup costs typically deliver better economics. This cost differential explains why prototyping vs production: Choosing EDM or CNC decisions often lean toward CNC for larger quantities of moderate-complexity parts in conventional materials.
Which Process Delivers The Surface Finish Your Application Needs?
Surface quality requirements represent another critical factor that can immediately determine your optimal manufacturing approach.
Understanding the surface finish Ra values for EDM and CNC capabilities reveals significant differences: EDM consistently achieves Ra 0.2-0.8μm with minimal post-processing requirements, creating a distinctive matte texture with excellent wear characteristics. CNC milling, while capable of good finishes, typically requires secondary grinding operations to achieve Ra values below 1.6μm for precision applications.

Exploring application-specific requirements further clarifies the selection process. Medical implants benefit from EDM's consistent, biocompatible finishes that avoid the microscopic tool marks that can harbor bacteria. Aerospace components with fatigue-critical surfaces often require the compressive stress characteristics of properly executed CNC machining. For both processes, achieving optimal surface finish results requires expertise and proper process control.
Conclusion
Selecting between EDM and CNC milling requires careful evaluation of your specific application requirements. For materials like titanium, the question of "Titanium machining: EDM or CNC?" depends entirely on your part's geometry, tolerance requirements, and production volume.
EDM delivers unmatched precision for hardened materials and complex internal geometries but comes with higher setup costs and longer processing times. CNC milling offers faster material removal rates and greater material versatility at generally lower costs for conventional materials and external features.
For optimal results, consider partnering with ISO 9001-certified precision machining services that offer both capabilities under one roof. The most sophisticated manufacturing operations frequently employ hybrid approaches—using EDM for critical features while leveraging CNC for the bulk of material removal—to achieve optimal quality, timeline, and cost balance.
Additional Resources
[Cost of EDM wire cutting vs CNC milling][^1]
[Surface finish Ra values for EDM and CNC][^2]
[Titanium machining: EDM or CNC][^3]
---
[^1]: Understanding the cost differences can help you make informed decisions for your machining projects.
[^2]: Exploring this will provide insights into the quality and precision of each machining method.
[^3]: This resource will help you determine the most effective machining method for titanium, enhancing your project outcomes.
-
Posted in
CNC milling, EDM





